Parametric thermal bridging assessment – Canadian Consulting Engineer

Image by Scott Armstrong.
As “per cent greater than code” is a fading metric, the design field has viewed the rise of a new effectiveness paradigm: thermal electrical power demand from customers depth (TEDI). Simply described, TEDI is the measure of heating power required to offset enclosure losses and to warmth fresh new air flow air. As a result, enclosure performance is no more time topic to trade-offs with remarkably effective mechanical methods. In truth, it’s paramount to accomplishing accomplishment.
TEDI has been adopted as a compliance metric for the Canada Eco-friendly Setting up Council’s (CaGBC’s) Zero Carbon Developing (ZCB) method and the Toronto Green Regular (TGS). It has also been a necessity of Passive Residence initiatives since that certification’s inception. Coupled with requirements to incorporate thermal bridging into complete-making effectiveness values, TEDI is switching the way consulting engineers style and build structures.
Layout strategies and efficiency
There is growing recognition in the style and building community of the relevance of obtaining a thermally effective constructing enclosure, with some provinces and municipalities referencing Passive Dwelling or the CaGBC ZCB normal. These programs consist of efficiency-centered targets for three major metrics: TEDI, whole electricity use depth (TEUI) and greenhouse fuel depth (GHGI). Creating enclosure efficiency influences each and every of these metrics, but is generally most apparent by way of TEDI.
TEDI accounts for the energy essential to offset enclosure gains and losses and to mood air flow air. Spaces necessitating higher air flow prices, these types of as laboratories and hospitals, can overwhelm enclosure-associated TEDI actions, but these styles of properties however reward from thermally effective enclosures by improving their resilience to alternate takes advantage of, ensuring passive survivability, improving upon occupant comfort and ease and enabling minimal-electrical power mechanical HVAC techniques.
Very low-strength HVAC units also assistance gasoline switching, which can significantly lower a project’s operational carbon emissions.

There is growing awareness in the design and style and building neighborhood of the importance of obtaining a thermally successful constructing enclosure. Image by Andrea Yee, courtesy WSP.
Solar heat gain
TEDI can be improved (i.e. minimized) by including higher solar heat obtain glazing balanced with fixed or dynamic shading. This technique helps optimize passive photo voltaic gains in the wintertime, then cuts down photo voltaic attain and overheating in summer season.
These techniques need to be refined following a more in-depth photo voltaic analyze for a proposed style, but some alternatives (applicable in just Ontario’s Golden Horseshoe) involve:
- increased solar obtain with dynamic or fastened shading on the south elevation to control overheating.
- lower solar warmth attain or dynamic glazing units on the east and west elevations.
- larger photo voltaic obtain on the north elevation with out shading.
Wellness-oriented spaces, like eateries, exercise rooms, gyms and meditation/yoga rooms, could also reward from more substantial windows and connected sights, daylight and passive photo voltaic heating. Hallways with more substantial glazed parts could also be viewed as along the south façade as a buffer for open or closed workplaces, benefiting from controlled solar warmth get in the winter season.
Glare problems from big spans of glazing can be mitigated by using reduce noticeable mild transmittance, dynamic glazing, diffuse glazing or inventive shading methods. Consideration could also be provided for ‘cascading’ conditioning of unique spaces or redistribution of vitality in between compatible areas.
Spaces like gyms could reward from bigger home windows.
It is vital to realize the photo voltaic exposure for every single web page and the effect of geographic site, setting up orientation, constructing variety and adjacent/ overshadowing conditions. These distinctive areas for just about every website could also notify the façade style and design, by incorporating bespoke shading methods. One example would be a customized exterior shade profile that traces the line of optimum premier solar obtain, providing architectural expression to weather adaptation.
Very glazed façade assemblies have to be thermally productive to stay away from offsetting passive heating added benefits. Passive photo voltaic rewards can be accomplished with modest glazing ratios and by balancing the highly glazed façades with opaque walls.
Adding far more insulation will not essentially outcome in dramatically much more productive assemblies.
Thermal bridging outcomes
Thermal bridging takes place when warmth stream bypasses insulated building enclosure components by means of remarkably conductive elements, cutting down the total helpful thermal benefit of the enclosure and building awkward residing ailments for occupants.
Most electricity analyses account for thermal bridging only by distinct field wall assemblies (e.g. cladding attachments) and standard Nationwide Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) window assemblies. However, plans like the Nationwide Energy Code for Buildings (NECB) 2015, TGS, Passive Property and CaGBC’s ZCB require groups to account for other standard and irregular thermal bridging, which include:
- linear ailments (projecting concrete ground slabs, parapets, masonry shelf angles, window-to-wall transitions and developing corners).
- level circumstances (structural penetrations, shade supports and roof anchors).
There is escalating demand from customers for detailed analyses that consist of these components. As designers, it is essential for consulting engineers to use the identical terminology when speaking about an enclosure’s thermal overall performance.
Apart from supplying exact enter knowledge for electrical power modelling, a thermal bridging investigation can deliver direction for enhancing the thermal performance of the making envelope through tiny style modifications.
Knowledge exhibits the thermal bridging impact of typical practice detailing can lower the genuine efficiency of a apparent area thermal worth by upward of 50%. The reduction is a lot more pronounced for increased very clear industry thermal values.
Incorporating more insulation will not essentially consequence in radically extra economical assemblies. It is critical to deal with the thermal bridge. Conducting a parametric or sensitivity assessment of thermal bridging problems can assistance establish in which depth updates may perhaps make the most reward to a specified project. The next are some examples:
- Introducing a thermal crack can assistance to mitigate heat loss by way of the slab.
- Steady insulation layers ought to be ensured at junctions, these types of as corners, parapets and wall style transitions.
- Bridging elements on the exterior, such as structural penetrations, need to be insulated.
This level of assessment has led to conversations of omitting a next electrical power recovery ventilator (ERV) in a household suite, removing perimeter heating in industrial buildings or targetinga better tier as per TGS (i.e. Tier 2 in its place of Tier 1). This flips the script on conventional discussions about whether enclosure upgrades are truly worth undertaking at all.
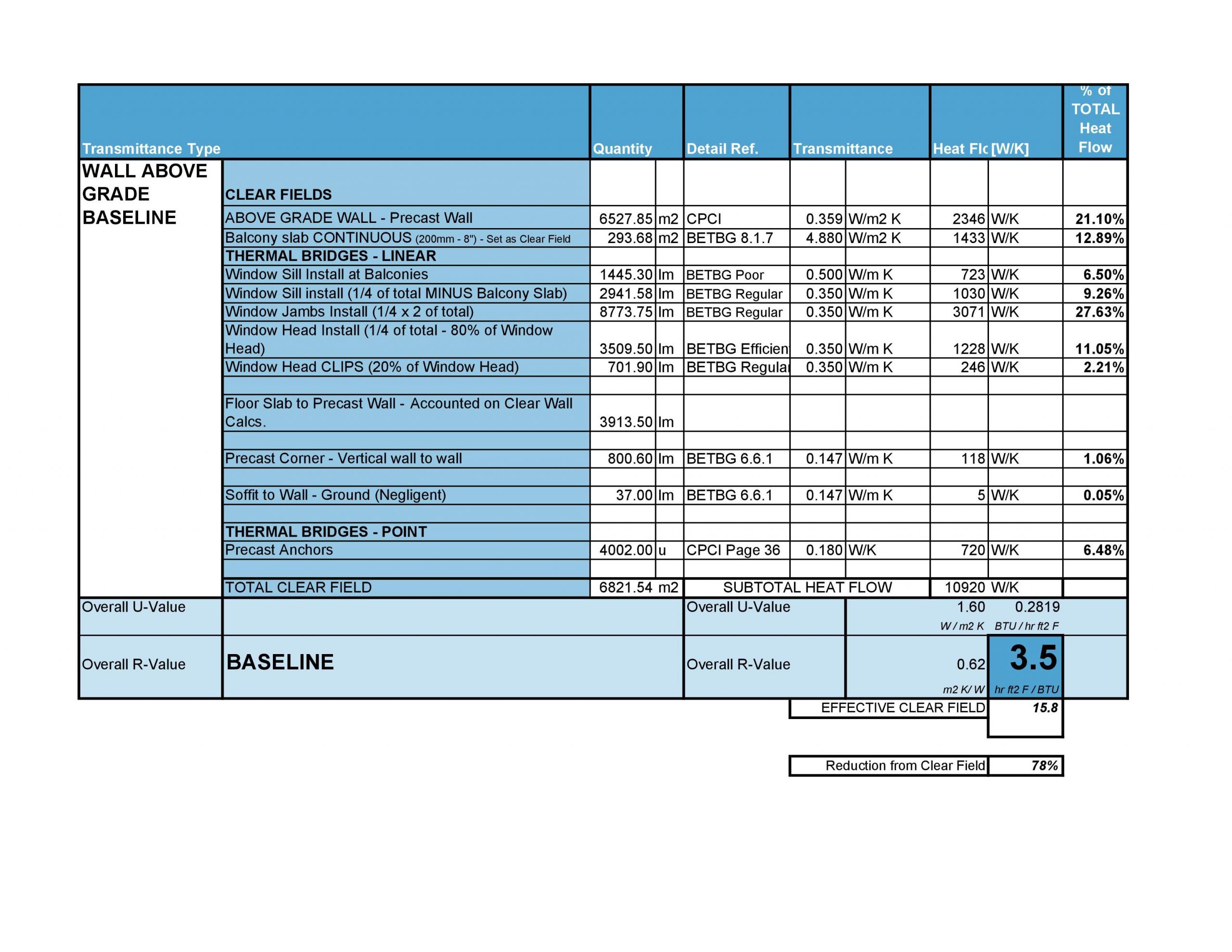
Chart 1.
Creating enhancements
Chart 1 supplies an overview of the thermal bridging evaluation for a typical mid-increase multi-unit household creating (MURB) in Toronto, focusing on above-grade opaque wall assemblies. The assembly for this job consists of a precast cladding panel with an efficient R-16 very clear subject thermal value.
Factoring in the thermal bridging from panel anchors, creating corners, balcony slabs and window perimeters, the very clear-industry R-16 is diminished to a complete-wall R-3.5. That is a 78% reduction in thermal general performance!
The subsequent are a several of the essential findings of the evaluation:
- Insulated precast panels, comprising 96% of the complete area place of the opaque enclosure, account for only 21% of complete heat movement.
- Precast anchors account for approximately 6.5% of whole warmth movement.
- Balcony slabs account for approximately 13% of complete heat movement.
- Window perimeters account for approximately 57% of total heat movement.
- Developing corners and soffit interfaces account for a bit extra than 1% of full heat stream.
This facts can help steer interest to the detail that most substantially influences thermal performance in this creating: the window perimeter.
Making use of thermal modelling software package, it is probable to make advancements to the specifics and estimate challenge-unique linear transmittance (PSI or ψ) values for the window-to-wall interface depth or point transmittance (CHI or χ) values for penetrations.
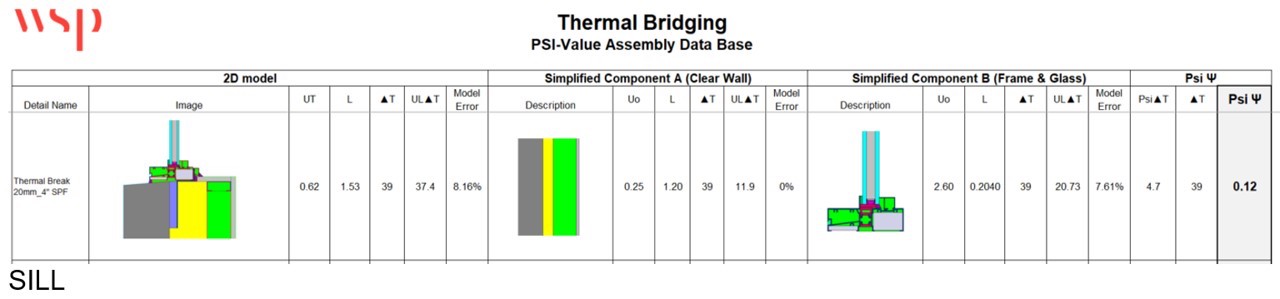
Chart 2.
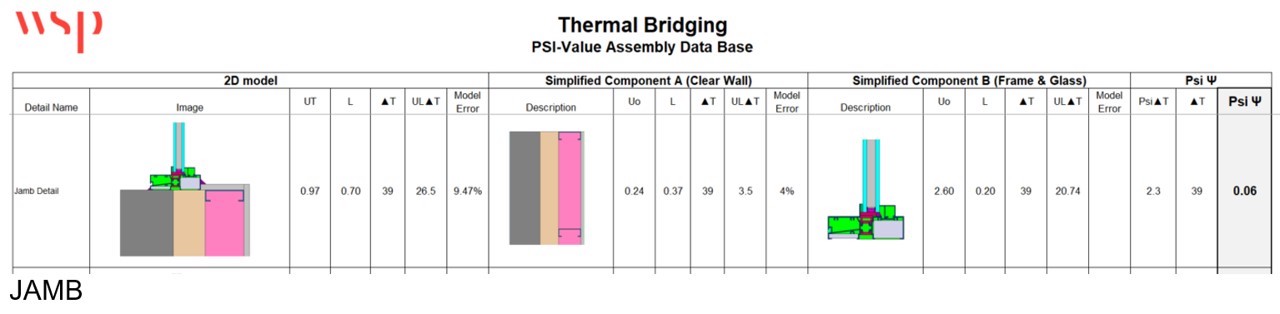
Chart 3.
Charts 2 and 3 illustrate the process for deciding personalized linear transmittance values for project-particular situations. Based on this data, the ψ value for the window perimeter can be decreased from .35 W/m K to .06 W/m K for the jamb and head and .12 W/m K for the sill. Substituting these values into the thermal bridging analysis demonstrates the impact of adding a thermal split at the window anchor and corresponding enhancement in complete-wall thermal value see Chart 4.
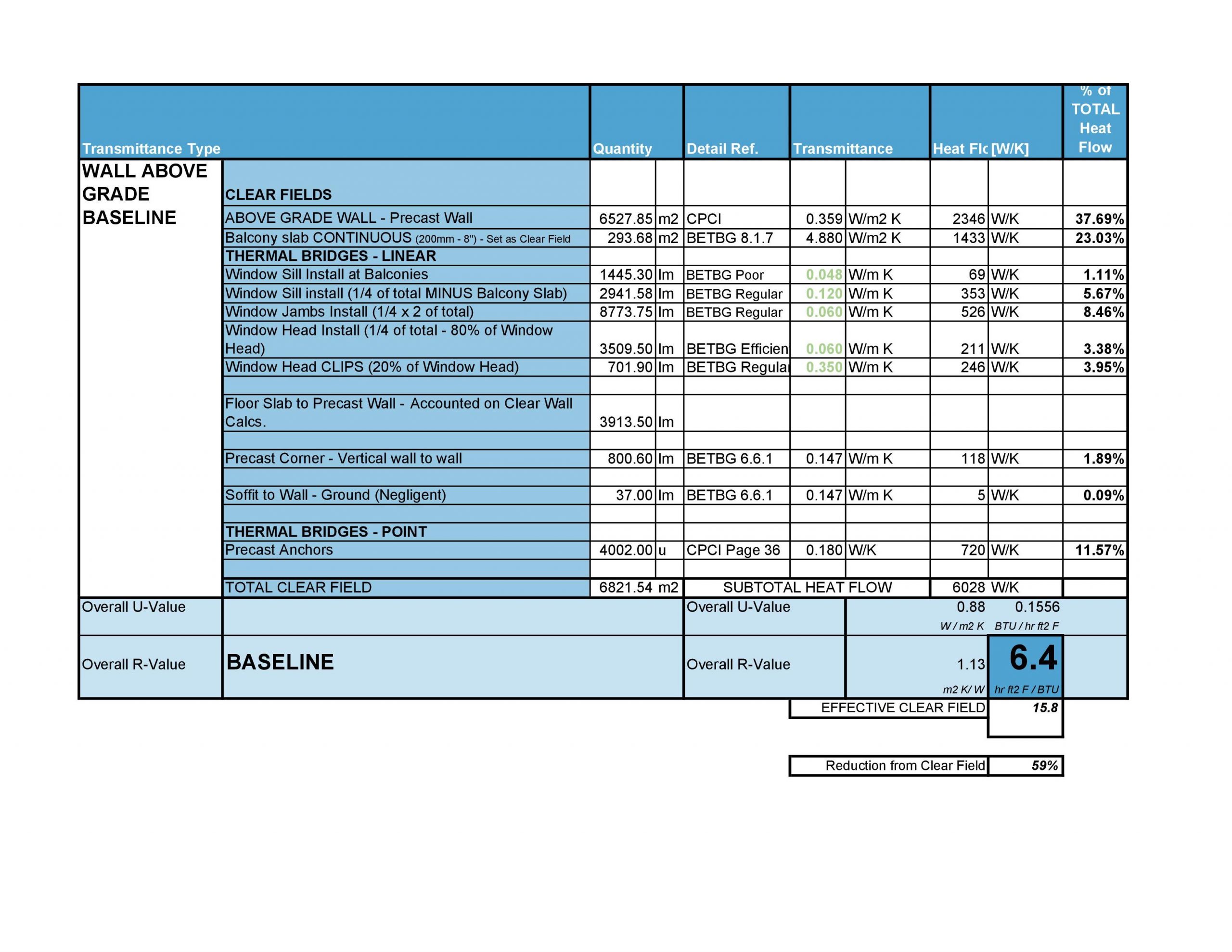
Chart 4.
This single depth improvement success in a around doubling of the full wall R-worth! This is the electric power of parametric thermal bridging evaluation.
It is feasible to parameterize specific aspects in this evaluation in a computation layout workflow, including elements in just the aspects and the thermal modelling course of action itself. Doing so could minimize the time wanted for personalized modelling, notably in the early style phases when fewer facts are readily available.
The time is suitable
Reduced-energy, low-carbon buildings demand from customers thermally productive making enclosures. Examining these structures making use of electrical power modelling equipment calls for precise metrics for their enclosures’ thermal overall performance.
Doing a parametric analysis of thermal bridging ailments will allow design and style and development teams to realize the results of seemingly minor facts on the all round thermal benefit. This system also helps groups regulate significant choices about enclosure style and design, introducing thermal breaks where needed to enhance overall performance.
As code and community jurisdictions introduce prerequisites for comprehensive thermal bridging examination, the time is ideal to integrate this method into far more initiatives.
Scott Armstrong is a senior façade specialist with WSP in Canada. For extra data, speak to him at [email protected].
This write-up at first appeared in the July/August 2021 issue of Canadian Consulting Engineer.





